The DETECTLANGUAGE function is a powerful and easy-to-use feature in Google Sheets that enables users to automatically detect the language of a given text or cell.
This function is particularly useful when working with multilingual datasets, as it allows users to quickly identify the language used in the text, which can then be used for various applications such as translation, sorting, filtering, or analysis.
DETECTLANGUAGE Syntax
The DETECTLANGUAGE function in Google Sheets has a simple syntax that takes only 1 argument. The basic syntax for the function is as follows:
=DETECTLANGUAGE(text)
Where:
text: This is the text or cell reference for which you want to detect the language.
Here are a few examples of how to use the DETECTLANGUAGE function with different input types:
Detect the language of a text string directly:
=DETECTLANGUAGE("Boungiorno, come stai?")
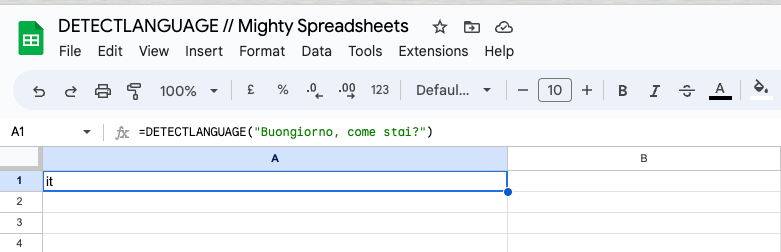
This formula will return “it” as the detected language, which stands for Italian.
Detect the language of a single cell:
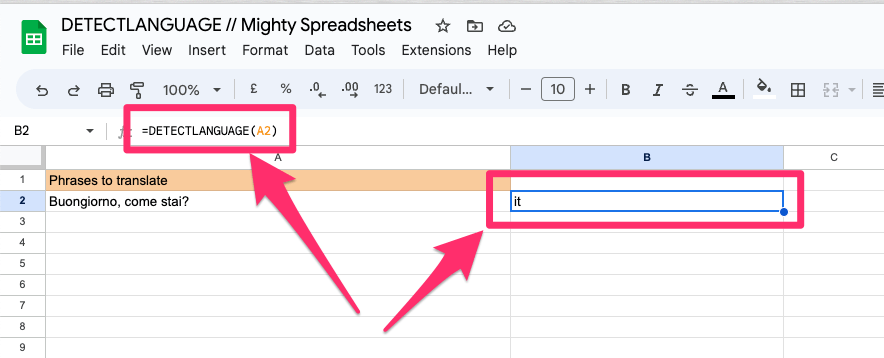
=DETECTLANGUAGE(A2)
Assuming cell A2 contains the text “Boungiorno, come stai?”, this formula will return “it” as the detected language, which stands for Italian.
Detect the language of a range of cells:
=DETECTLANGUAGE(A2:A4)
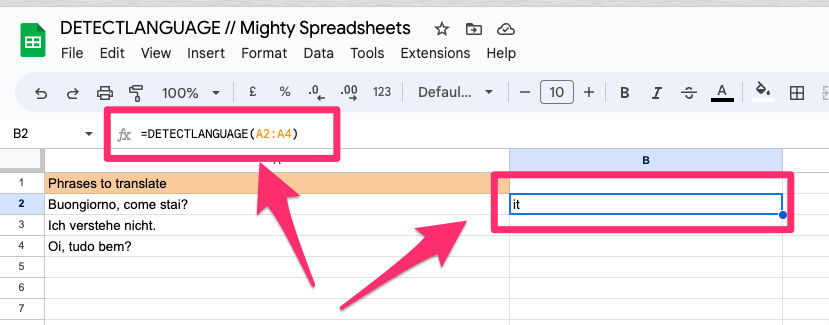
If there are multiple languages in the specified range, only the first language will be returned.
A few things to note:
- Remember that the DETECTLANGUAGE function will return the language code according to the ISO 639-1 standard, which consists of a two-letter code for each language.
- In case the input text is empty, it will return an error: “#Value” with a “Function DETECTLANGUAGE parameter 1 value should not be empty.” notification.
- If the provided text is a random string of characters the output returned will default to “en” which is not useful feedback
- Limitations: Although DETECTLANGUAGE supports a wide range of languages, it may not accurately identify languages with similar scripts or dialects.
Practical Examples and Use Cases
Sorting or Filtering Data by Language
Let’s imagine that you have a dataset containing user-generated content in multiple languages.
You can use the DETECTLANGUAGE function to identify the language of each entry and create a new column with the detected language code.
Then, you can sort or filter the data based on the language column.
Step 1: In column A, you have the text entries.
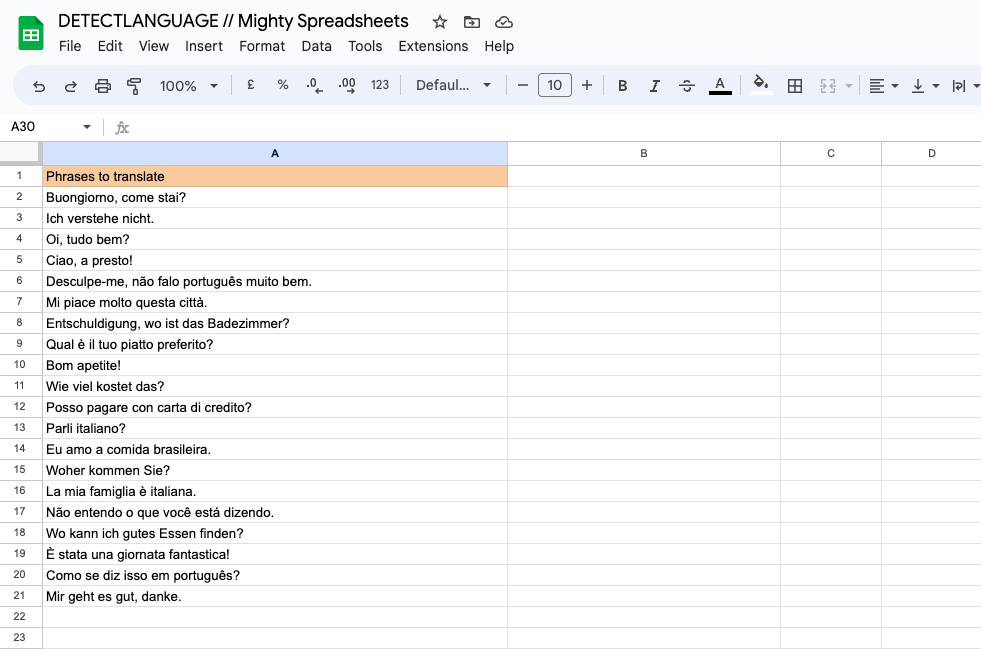
Step 2: In column B, use the formula =DETECTLANGUAGE(A1) and apply it to all rows with data.
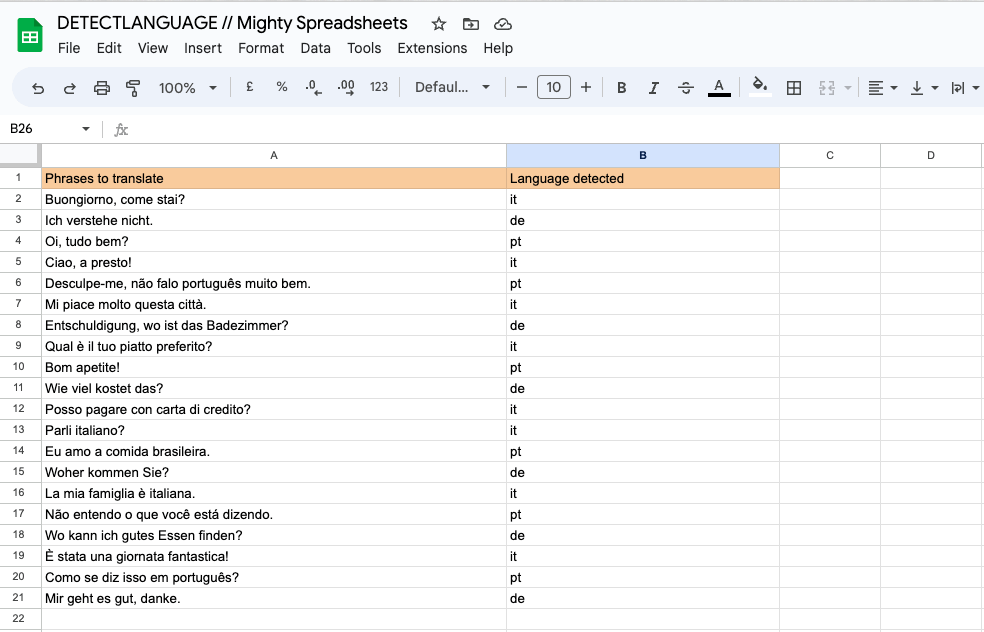
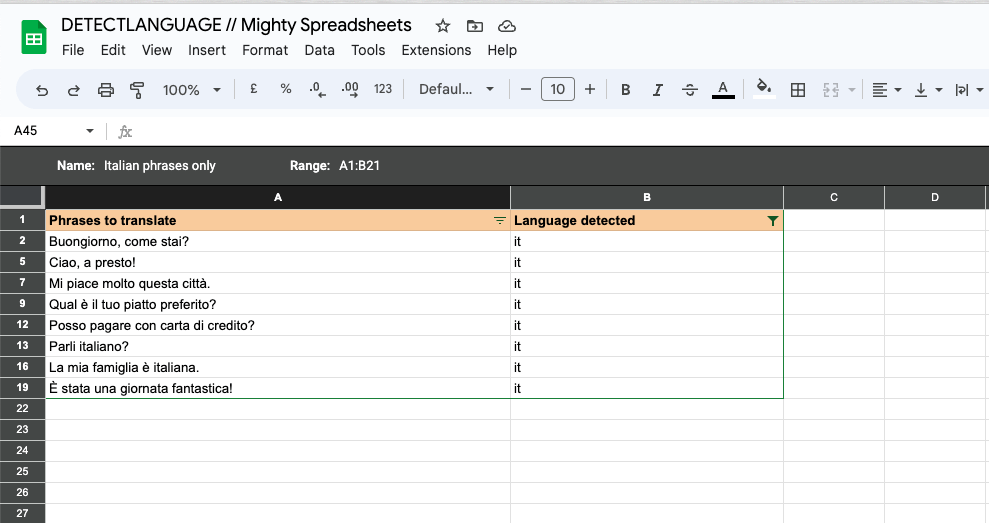
Step 3: Now, you can sort or filter your dataset using the detected language codes in column B.
Read next: Learn more on filtering data in Google Sheets
3 Other Best Cases to use DETECTLANGUAGE function
Content Moderation
If you need to moderate user-generated content in different languages, DETECTLANGUAGE can help identify the language used.
International Marketing
DETECTLANGUAGE is also helpful when assessing the language diversity of your target audience, guiding language-based marketing strategies, and creating tailored content for different language groups.
Sentiment Analysis
DETECTLANGUAGE can preprocess customer reviews or feedback in multiple languages, helping you conduct more accurate sentiment analysis by language.
3 Cases When DETECTLANGUAGE Shouldn’t Be Used
Ambiguous or Similar Languages
DETECTLANGUAGE has many benefits, but it may not work well for languages that are similar or ambiguous. In such cases, you may need to use a more specialized language detection tool.
Large Datasets with Performance Concerns:
When working with large datasets, DETECTLANGUAGE can slow down the spreadsheet, so consider optimizing its usage or using alternative methods if performance is a concern.
Language Identification for Translation Purposes Only
If you’re only interested in translating the text, you can use the GOOGLETRANSLATE function without specifying the source language, as it automatically detects the language for translation.
Your Takeaways from this article:
- DETECTLANGUAGE function detects the language of a given text or cell reference.
- It can be applied in many contexts. It can be used for sorting, filtering, or analyzing multilingual datasets, content moderation, international marketing, and sentiment analysis.
- The function returns a language code according to the ISO 639-1 standard, which consists of a two-letter code for each language.
- DETECTLANGUAGE may not accurately identify languages with similar scripts or dialects.
- The function may not work well for large datasets, so consider optimizing its usage or using alternative methods such as putting the output in plain text
- If you’re only interested in translating the text, you can use the GOOGLETRANSLATE function and set the source language to “auto”.
